
The Canadian Homeowner's Guide to Solar Azimuth and Tilt: Orientation by Region
Explain orientation fundamentals using Canadian latitude bands; contrast south-facing defaults with east/west trade-offs; show how winter optimization works in northern regions.
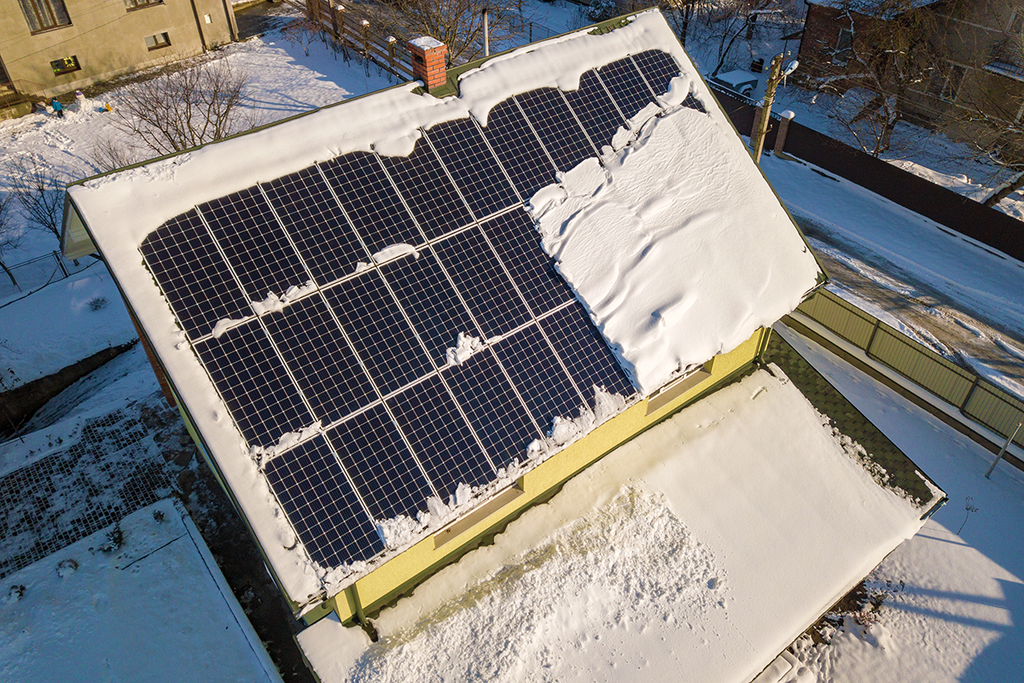

Beating Winter: Optimizing PV Tilt and Orientation for Canadian Snow Seasons
Provide winter-focused strategy: tilt ≈ latitude + 10°, slight west azimuth, and snow-shedding tactics; explain when winter bias makes sense for Canadian climates.
Shading Done Right: Site Assessment and Tools for Canadian Homes
Practical how-to for shading analysis; highlight tools (Solar Pathfinder, software/drones), common obstructions, and mitigations for Canadian residential installations.

Roof Design for PV: Pathways, Setbacks, and Materials in Canada
Translate PV-ready roof design into builder's checklist; explain ridge setbacks and access pathways by roof type; roofing materials and attachment; conduit planning.
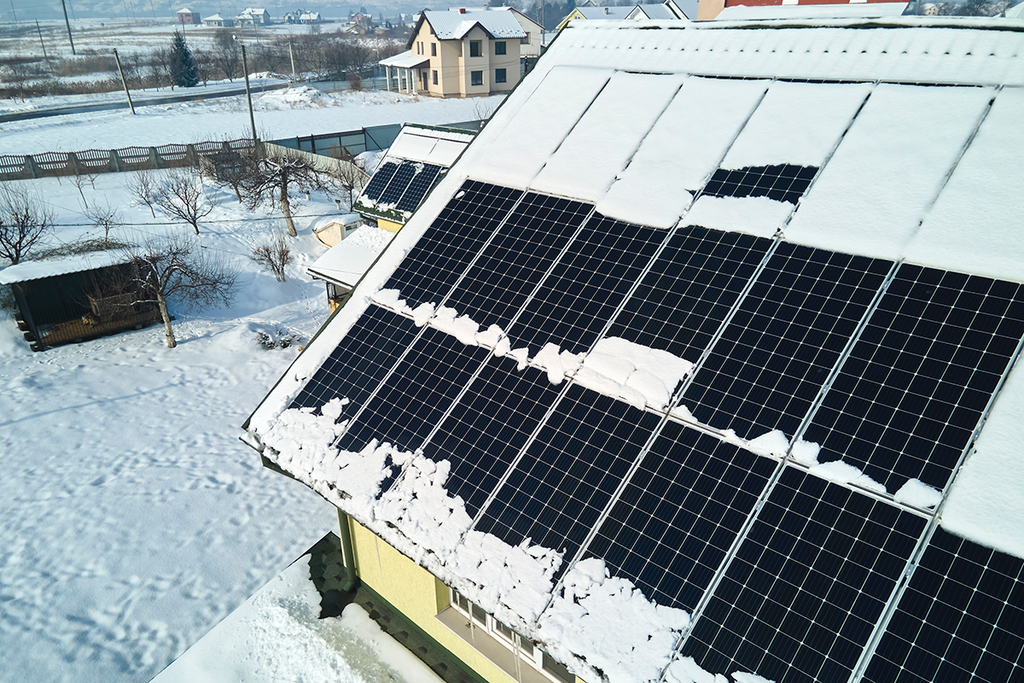

When Snow Meets Solar: NBCC 2020 Snow Loads and Roof-Mounted PV
Decode NBCC 2020 Article 4.1.6.16 and Structural Commentaries for roofs with panels; focus on sliding impedance, accumulation and drift factors, and design workflow.

Ground-Mount or Roof-Mount? Choosing the Right System for Canadian Homes
Decision framework comparing roof and ground systems in Canada, balancing cost, performance, snow management, access, and environmental footprint considerations.

Electrical Ready: CEC Rule 64-112, Panel Sizing, and PV Conduits
Make the electrical panel ready for PV; illustrate Rule 64-112 calculations, busbar vs main breaker considerations, conduit sizing, and inverter wall space requirements.

Mapping the Sun: Using NRCan's PV Potential Maps to Size Your System
Walkthrough of NRCan's mapping application: finding PV potential by municipality and orientation, interpreting monthly vs annual values, and validating tilt choices for Canadian locations.

PV on Metal Roofs: Attachment Methods and Cold-Climate Performance
Best practices for attaching PV to standing seam and other metal roofs; durability, thermal movement, and service life considerations in Canadian climates.

From Plans to Permit: How to Prepare a PV-Ready Home in Canada
Home builder's and designer's checklist to implement PV-ready features early—roof areas, setbacks, conduits, wall space, and panel capacity—for cost-effective later PV installation.

Winter Operating Tips: Temperature Coefficients, Snow Management, and Maintenance
Explain PV module temperature behavior and how cold Canadian winters can be beneficial; outline snow management strategies; discuss maintenance access and safety protocols.